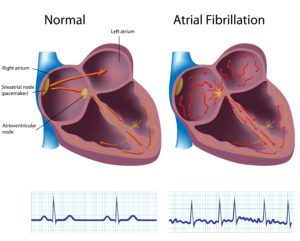
There are about 500,000 people in the UK with the condition and it is the most common heart rhythm disturbance. It can affect adults of any age but it is more common in older people and more in men than women. About 10% of over 75’s have the condition and the risk is increased in people who excessively smoke or drink. It is also more likely to affect people with high blood pressure, heart valve problems and other conditions.
Symptoms
- Fast, irregular heartbeat
- Breathlessness
- Dizziness
- Chest pain
Sometimes, however, there are no signs or symptoms.
Types of Atrial Fibrillation
There are different types of this condition and they have different effects on the patient.
- Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation — this comes and goes and usually stops within 48 hours without any treatment
- Persistent atrial fibrillation – this lasts for longer than seven days (or less when it is treated)
- Longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation – this usually lasts for longer than a year
- Permanent atrial fibrillation – this is present all the time and there are no more attempts to restore normal heart rhythm
Although uncomfortable at times, someone with Atrial Fibrillation can lead a normal life and the condition can be controlled with medication. However, it does increase their risk of stroke. Treatment can vary depending on the person but includes medications to control it, medicines to reduce the risk of a stroke, cardioversion (electric shock treatment), catheter ablation or having a pacemaker fitted.
For more information on training courses, visit our “Courses” page which also includes our First Responder and First Person on Scene (FPOS) Courses.

