The human tongue is one of the most fascinating and complex organs in the body. It is a muscular organ that is located in the mouth and is responsible for a wide range of functions, including tasting, speaking, and swallowing. The tongue is made up of a combination of muscles, nerves, and taste buds. It […]
Anatomical Terminology
Utilising precise anatomical terminology allows for accurate identification and communication regarding body parts and injuries. The standard reference is the anatomical position: standing upright with palms facing forward. Key terms include:
- Anterior: In front of.
- Posterior: Behind.
- Proximal: Nearest to the point of origin.
- Distal: Furthest from the point of origin.
- Superior: Above or higher.
- Inferior: Below or lower.
- Medial: Towards the midline.
- Lateral: Away from the midline.
Familiarity with these terms enhances the ability to describe locations and relationships of body parts accurately.
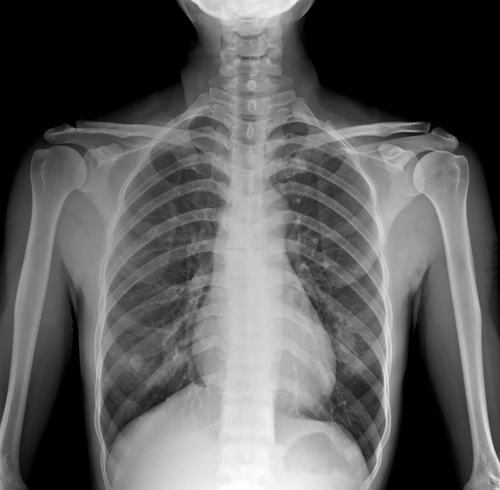
Major Organs and Their Functions
The Heart
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products. It operates through a coordinated electrical system that ensures rhythmic contractions. :contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}
The Lungs
The lungs facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and the bloodstream, playing a crucial role in respiration.
The Kidneys
Kidneys filter blood to remove waste products and excess fluids, maintaining electrolyte balance and regulating blood pressure.
The Spleen
The spleen plays a vital role in the immune system by filtering blood, recycling red blood cells, and storing white blood cells and platelets.
The Appendix
The appendix is a small, tube-like organ located in the lower right side of the abdomen. While its exact function is not entirely clear, it is believed to play a role in the immune system.
The Bladder
The bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores urine before it is excreted from the body.
First Aid Considerations
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
In cases of cardiac arrest, performing CPR helps maintain blood flow to vital organs until professional medical assistance arrives. The process involves chest compressions and rescue breaths to support heart and lung function. :contentReference[oaicite:2]{index=2}
Pulse Points
Identifying pulse points is essential for assessing circulation and administering certain first aid techniques. The primary pulse point is the radial pulse, located on the wrist. :contentReference[oaicite:3]{index=3}
Managing Serious Bleeding
Controlling severe bleeding promptly is critical to prevent shock and other complications. Applying direct pressure to the wound and using appropriate bandaging techniques are fundamental first aid responses. :contentReference[oaicite:4]{index=4}
Further Resources
Expand your knowledge on human anatomy and first aid:
For comprehensive first aid training, enrol in our First Aid at Work Annual Refresher (VTQ) course.