Blast injuries are much more common than you may think. They can come from many different places – not just bomb explosions. They can also arise from house fires, in-cylinder fires or basically when anything explodes. When assessing how bad an explosion has been, there are a few factors that need to be considered: how […]
Burns are injuries to the skin or deeper tissues caused by contact with heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. Prompt and appropriate first aid can significantly impact healing and reduce complications.
Types of Burns
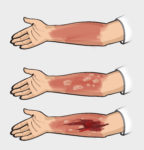
Burns are classified based on their depth and severity:
- Superficial (First-Degree) Burns: Affect only the outer layer of the skin, causing redness and pain. Sunburn is a common example.
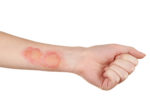
- Partial-Thickness (Second-Degree) Burns: Involve the first and second layers of skin, leading to blisters, swelling, and intense pain.
- Full-Thickness (Third-Degree) Burns: Extend through all layers of the skin, potentially affecting underlying tissues. The area may appear white, charred, or leathery, and sensation may be lost due to nerve damage.
Immediate First Aid Steps
For effective burn management:
- Stop the Burning Process: Remove the person from the source of the burn safely.
- Cool the Burn: Place the affected area under cool running water for at least 20 minutes to reduce pain and swelling. Avoid using ice or very cold water. Learn more about cooling burns and using cling film.
- Protect the Burn: After cooling, cover the burn with a sterile, non-stick dressing or clean cloth to protect it from infection.
- Remove Constrictive Items: Gently remove jewellery, belts, or tight clothing from the affected area before swelling occurs.
- Avoid Home Remedies: Do not apply creams, oils, or other substances to severe burns, as they can cause infection.
- Seek Medical Attention: For burns larger than the size of the victim’s hand, or those affecting the face, hands, feet, groin, or major joints, seek professional medical care immediately.
Special Considerations
Certain types of burns require additional care:
- Chemical Burns: Remove contaminated clothing and rinse the affected area under running water for at least 20 minutes. Avoid neutralising the chemical unless instructed by a professional.
- Electrical Burns: Ensure the source of electricity is turned off before assisting. Electrical burns can cause internal injuries; seek medical attention even if the external damage appears minor. Understand more about electrical injuries.
- Clothing on Fire: Stop the person from running, drop them to the ground, and roll them to extinguish flames. Use a blanket or heavy fabric if available, then cool the burn with water.
Preventing Burns
To reduce the risk of burns:
- In the Kitchen: Keep pot handles turned inward, use oven mitts, and supervise children closely.
- Electrical Safety: Regularly check for faulty wiring, avoid overloading sockets, and keep appliances away from water.
- Chemical Handling: Use protective gear and follow safety instructions when working with hazardous substances.
- Fire Safety: Install smoke detectors, keep a fire extinguisher accessible, and practice emergency evacuation plans.
Further Resources
Enhance your knowledge of burn management:
- Burns Treatment – Using Cling Film
- Burns and Burn Kits
- Electrical Injuries
- Cleaning Products Poisoning
- Poisons
For comprehensive first aid training, consider enrolling in our First Aid at Work Annual Refresher (VTQ) course.