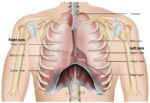
Closed chest injuries can be inherently serious, as the chest houses many critical organs, such as the heart, lungs, and many major blood vessels. A closed chest injury could be where someone in a car accident and hit their chest hard on the steering wheel. Most chest trauma injuries will need urgent medical attention. Always call for […]
Chest Injuries
Chest injuries can be serious, as the chest houses critical organs such as the heart and lungs. They can result from blunt force trauma or penetrating injuries.
Symptoms
- Difficulty breathing
- Chest pain
- Cyanosis (bluish skin due to lack of oxygen)
- Uneven chest movement
- Coughing up blood
First Aid Response
- Call Emergency Services: Dial 999 or 112 immediately.
- Ensure the Person is Comfortable: Help them sit in a position that eases breathing.
- Apply Pressure to Wounds: If there is an open wound, cover it with a sterile dressing and apply gentle pressure.
- Monitor Vital Signs: Keep track of their breathing and consciousness until help arrives.
For detailed information on chest injuries and their management, refer to the Chest Injuries page.
Internal Bleeding
Internal bleeding occurs when blood leaks from blood vessels inside the body, often due to trauma or medical conditions. It can be life-threatening if not promptly addressed.
Symptoms
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Dizziness or fainting
- Pale, clammy skin
- Shortness of breath
- Unexplained bruising
First Aid Response
- Call Emergency Services: Dial 999 or 112 immediately.
- Keep the Person Still: Encourage them to lie down and stay as still as possible to prevent further injury.
- Monitor Vital Signs: Observe their breathing and level of consciousness.
- Provide Reassurance: Keep them calm and informed until medical help arrives.
For more information on internal bleeding and its management, visit the Internal Bleeding page.
Knife Wounds
Knife wounds are penetrating injuries that can cause significant damage to tissues and organs. Immediate and appropriate first aid is essential to manage bleeding and prevent infection.
Symptoms
- Visible puncture wound
- Bleeding
- Swelling and redness around the injury
- Pain at the injury site
- Signs of shock (e.g., rapid heartbeat, clammy skin)
First Aid Response
- Ensure Scene Safety: Confirm that the area is safe before approaching the injured person.
- Call Emergency Services: Dial 999 or 112 immediately.
- Control Bleeding: Apply direct pressure to the wound using a sterile dressing or clean cloth.
- Stabilise Embedded Objects: If the knife is still in place, do not remove it; instead, stabilise it with bandages to prevent movement.
- Monitor for Shock: Keep the person lying down, elevate their legs if possible, and cover them to maintain body temperature.
For detailed information on managing knife wounds, refer to the Knife Wounds page.
Strains and Sprains
Strains and sprains are common soft tissue injuries affecting muscles, tendons, and ligaments. While they are generally not life-threatening, they can cause significant pain and mobility issues.
Symptoms
- Pain and tenderness
- Swelling and bruising
- Limited range of motion
- Instability in the affected joint
First Aid Response
Follow the **RICE** method:
- Rest: Avoid putting weight on the injured area.
- Ice: Apply an ice pack wrapped in a cloth for 15-20 minutes every few hours.
- Compression: Use a bandage to provide support and reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Keep the injured limb elevated above heart level to reduce swelling.
If pain persists or the person cannot move the joint, seek medical advice. For more details, visit the Strains and Sprains page.